Initial Treatment Of Dka
Initial Treatment Of Dka. Appropriate treatment includes administering intravenous fluids and insulin, and monitoring glucose and The presentation of DKA varies with severity and comorbid conditions. Successful management of DKA and HHS requires meticulous moni-toring and recording of the patient's clinical and biochemical response to treatment so that timely. • Initial investigations should include: o Blood ketones o Capillary blood glucose o Venous plasma glucose o Urea and electrolytes o Venous blood Complication rate of DKA treatment (e.g.cerebral oedema) In hospital death rates In hospital complications cerebral oedema, pulmonary oedema, ARF.
The biochemical criteria for diagnosis of DKA are Guidelines for management of DKA.
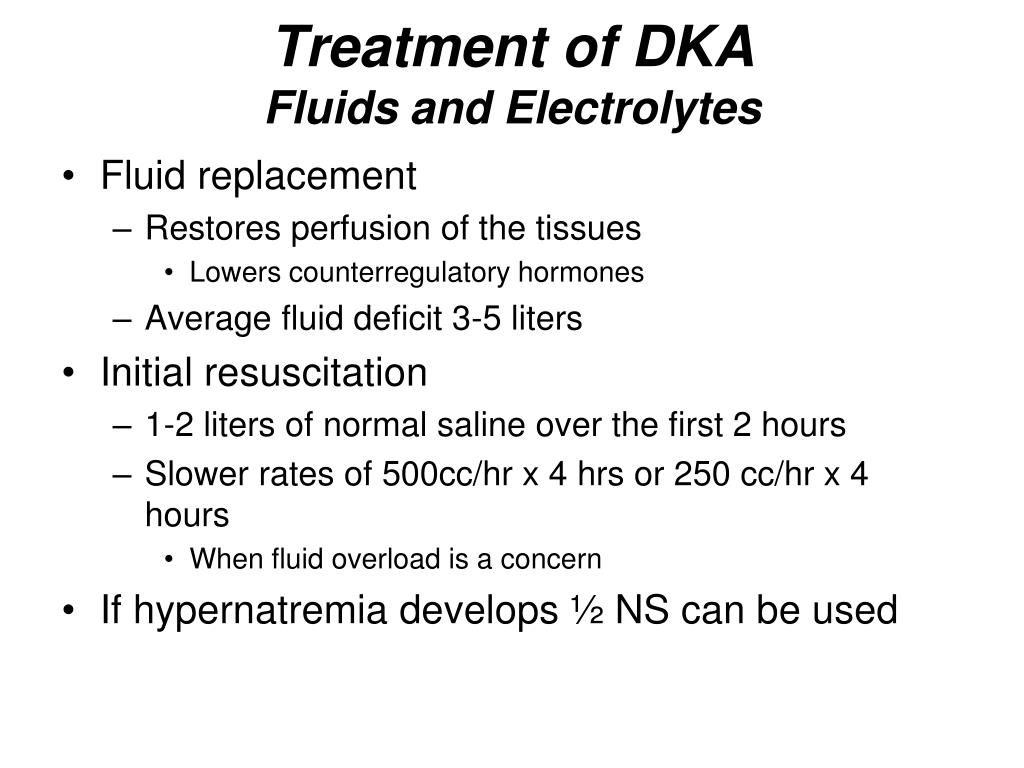
The initial treatment phase aims to restore circulating volume, reduce blood glucose levels, to correct any electrolyte imbalances and to reduce ketone Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is an acute episode which can present in those with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus.
1.Green Veggie Inflames Blood Sugar
2.Green Veggie Spikes Blood Sugar
3.Erratic Blood Sugar? Never Eat This Veggie
4.Erratic Blood Sugar? Avoid This “Healthy” Green Veggie
5.Green Veggie Deadly for Blood Sugar
There has been much discussion about the use of bicarbonate in the treatment of DKA with significant disparity in opinion. Diabetic Coma: Diabetic Ketoacidosis, Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State and. A low-dose insulin regimen has the advantage of not inducing the severe hypoglycemia or hypokalemia that may be observed with a.